First we did a recap on paper chromatography, and here are some things to note when carrying out the experiment.
- always use pencil to mark the line, not pen as pen contains ink
- solvent front: where the ink stop moving, the ink will not go beyond this line
- mobile phase: solvent (moving)
- stationary phase: paper (not moving)
- make sure the ink doesn't touch the pencil line
- solvent below pencil line so that the solutes would not be in contact with it
- ink does not dissolve well in water but dissolves well in ethanol
(Source: http://usefulchem.wikispaces.com/JanuPExp001 )
Rf Value = Distance moved by substance/ Distance moved by the solvent
Conditions that affects the results:
- Pressure
- Temperature ( for example, if you heat up the solvent, solubility will increase and the spot will be higher, thus more solvent will dissolve.
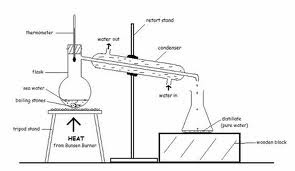
Simple Distillation
- Separate the solvent from a solution of so lute
- IMPORTANCE: Solvent is the main aim
- Distilled water: No ions at all, pure, however, if humans depend on distilled water, it is unhealthy since we need certain ion and compounds
- No evaporation
We were left with some question to do research on:
- What is the purpose of the boiling stone
- What does it mean by smooth boiling and/ or what happens if you do not have it?
- What is the condenser for?
- What is the thermometer for?
- Why is there are water inlet and water outlet? What purpose does their position serve?
1/2. What is the purpose of the boiling stone AND What does it mean by smooth boiling and/ or what happens if you do not have it?
- known as the boiling chips/ anti-bumping granules
- minute, unevenly shaped stones added to liquid so that they can boil easily
- fluids can boil easily without turning superheated
- without the, liquid heater in horizontal container might become superheater and 'bump' suddenly. discharging vapour occasionally
- reagents/ discharge may spill it it bumps
- made of absorbent matter eg alumina, calcium, carbonate, carbon, with non-reactive teflon which makes sure boiling chips offer effective nucleation spots
- What water is boiled in a close container known as a boiler, vapour evaporating from the surface of the boiling water passes through a pipe leading from the boiler to a vessel, called a condenser
- Positioning is crucial: entire mercury bulb must be positioned below the bottom of the orifice leading to the condenser
- Cold water is used to condense the gas to become liquid. It should not switch places because water out is hotter and hot water rises due to convection. If the water outlet is put below, the condenser would not work because the whole set-up will heat up and hence it does not serve its purpose.
Next Lesson: Practical- Separation Techniques

No comments:
Post a Comment